How to operate a drone? This seemingly simple question opens a world of possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to intricate precision maneuvers. Mastering drone operation requires understanding not only the basic controls but also the intricacies of drone technology, relevant regulations, and safety protocols. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to confidently navigate the skies, whether you’re a budding hobbyist or a seasoned professional.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating these steps requires a good understanding of the regulations and safety procedures. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including practical exercises, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Safe and responsible drone operation is crucial for both personal safety and the integrity of airspace.
We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and calibration to advanced flight techniques and troubleshooting common issues. Learn about different drone components, their functions, and how they interact to achieve stable and controlled flight. We’ll also delve into the legal aspects of drone operation, ensuring you fly responsibly and within the boundaries of the law. By the end, you’ll be ready to take to the skies with confidence and skill.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. Failure to do so can result in fines, legal action, and potential harm to people and property. This section Artikels essential safety procedures and regulatory information.
Drone Licensing and Permits
Drone regulations vary significantly by country and even within regions of a single country. Some countries have a tiered system, differentiating between recreational and commercial use, while others may have more unified rules. Generally, commercial drone operation necessitates a higher level of certification and adherence to stricter guidelines than recreational flying. It is crucial to research and understand the specific laws in your area before operating any drone.
For example, in the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires registration for most drones and may require a Part 107 Remote Pilot Certificate for commercial operations. In Europe, the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) sets standards for drone operation, and individual member states may have additional regulations. Always check with your national aviation authority for the most up-to-date information.
Drone Safety Procedures

Safe drone operation involves a multi-stage process encompassing pre-flight checks, in-flight awareness, and post-flight procedures. These procedures minimize risks and ensure both the drone and surrounding environment remain safe.
- Pre-flight: Check weather conditions, battery levels, GPS signal strength, and propeller integrity. Inspect the drone for any visible damage.
- During flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoid flying near airports or restricted airspace, and be mindful of obstacles and people.
- Post-flight: Secure the drone, power it down, and store it properly. Review flight logs and check for any damage.
Pre-flight Inspection Checklist
A thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for safe operation. This checklist helps ensure all systems are functioning correctly.
- Check battery level and charge.
- Inspect propellers for damage or wear.
- Verify GPS signal acquisition.
- Calibrate the compass.
- Check all control surfaces for proper function.
- Ensure all necessary safety features are enabled (e.g., Return-to-Home).
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
Commercial vs. Recreational Drone Regulations
The table below highlights key differences in regulations for commercial and recreational drone use.
| Aspect | Commercial Use | Recreational Use |
|---|---|---|
| Licensing | Usually requires a pilot’s license or certificate (e.g., Part 107 in the US) | May require registration but often not a pilot’s license |
| Operational Restrictions | Stricter restrictions on airspace, flight altitudes, and operational areas | Less stringent restrictions, but still subject to rules regarding airspace and safety |
| Insurance | Typically requires liability insurance | Insurance is often recommended but may not be mandatory |
| Operational Standards | Higher standards for maintenance, flight planning, and risk assessment | Simpler operational standards, but safety remains paramount |
Understanding Drone Components and Functions
A drone’s functionality stems from the coordinated operation of several key components. Understanding these components is essential for safe and effective operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone comprises several essential components, each playing a vital role in its operation. These include the frame, motors, propellers, electronic speed controllers (ESCs), flight controller, battery, GPS module, and camera (if equipped).
- Frame: Provides the structural support for all other components.
- Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to spin the propellers.
- Propellers: Generate thrust, enabling flight and maneuverability.
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Regulate the speed of each motor, allowing for precise control.
- Flight Controller: The brain of the drone, processing data from various sensors and controlling motor speeds to maintain stability and execute commands.
- Battery: Provides the power source for the drone’s operation.
- GPS Module: Enables precise positioning and navigation.
- Camera (if equipped): Captures photos and videos.
Drone Propeller Types and Their Impact
Different propeller designs influence flight performance, affecting aspects such as thrust, efficiency, and noise levels. Factors such as pitch, diameter, and number of blades contribute to these variations. For instance, larger propellers generally produce more thrust, while propellers with a higher pitch tend to be more efficient at higher speeds.
Learning to operate a drone involves understanding its controls and safety regulations. A crucial first step is familiarizing yourself with the basics, which can be readily achieved by consulting resources like this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. Mastering these fundamentals will ensure safe and responsible operation, allowing you to confidently explore the capabilities of your drone.
The Flight Controller’s Role

The flight controller is the central processing unit of the drone, integrating data from various sensors (such as gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers) and using this information to control the motors and maintain stability. It also receives commands from the remote controller and executes them accordingly, coordinating the drone’s movements in three dimensions.
Internal Workings of a Drone (Diagram)
Imagine a central box representing the flight controller. Four arms extend from this box, each supporting a motor and propeller. Wires connect the motors to the ESCs, and the ESCs are connected to the flight controller. The battery is usually mounted on the frame, close to the flight controller. A GPS module is attached, typically on top or underneath the frame, sending location data to the flight controller.
If equipped, the camera is usually mounted on a gimbal, connected to the flight controller for image stabilization.
Pre-Flight Procedures and Calibration: How To Operate A Drone
Before each flight, essential calibrations and checks are necessary to ensure safe and accurate operation. These procedures help avoid potential issues and enhance flight stability.
Step-by-Step Pre-flight Calibration and Checks
- Power on the drone and remote controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition (typically indicated by a visual cue on the remote controller).
- Calibrate the compass according to the drone’s instructions (usually involves rotating the drone 360 degrees).
- Check battery level and ensure sufficient charge for the planned flight duration.
- Inspect propellers and other components for damage.
- Perform a pre-flight motor test (usually a feature within the drone’s software).
- Select the appropriate flight mode.
Importance of GPS Signal Acquisition
GPS signal acquisition is crucial for precise positioning and flight stability, especially for features like Return-to-Home. Without a strong GPS signal, the drone’s location awareness may be compromised, potentially leading to inaccurate navigation and uncontrolled flight.
Compass Calibration and its Significance
Compass calibration ensures accurate heading information, vital for maintaining a stable flight path and executing precise maneuvers. Inaccurate compass readings can cause the drone to drift or deviate from the intended course.
Pre-flight Actions Checklist (Order of Importance)
- Check weather conditions and airspace restrictions.
- Check battery level and charge.
- Acquire GPS signal.
- Calibrate compass.
- Inspect drone for damage.
- Perform pre-flight motor test.
- Power on remote controller and drone.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is fundamental to safe and effective drone operation. This section details the core controls and maneuvers essential for every pilot.
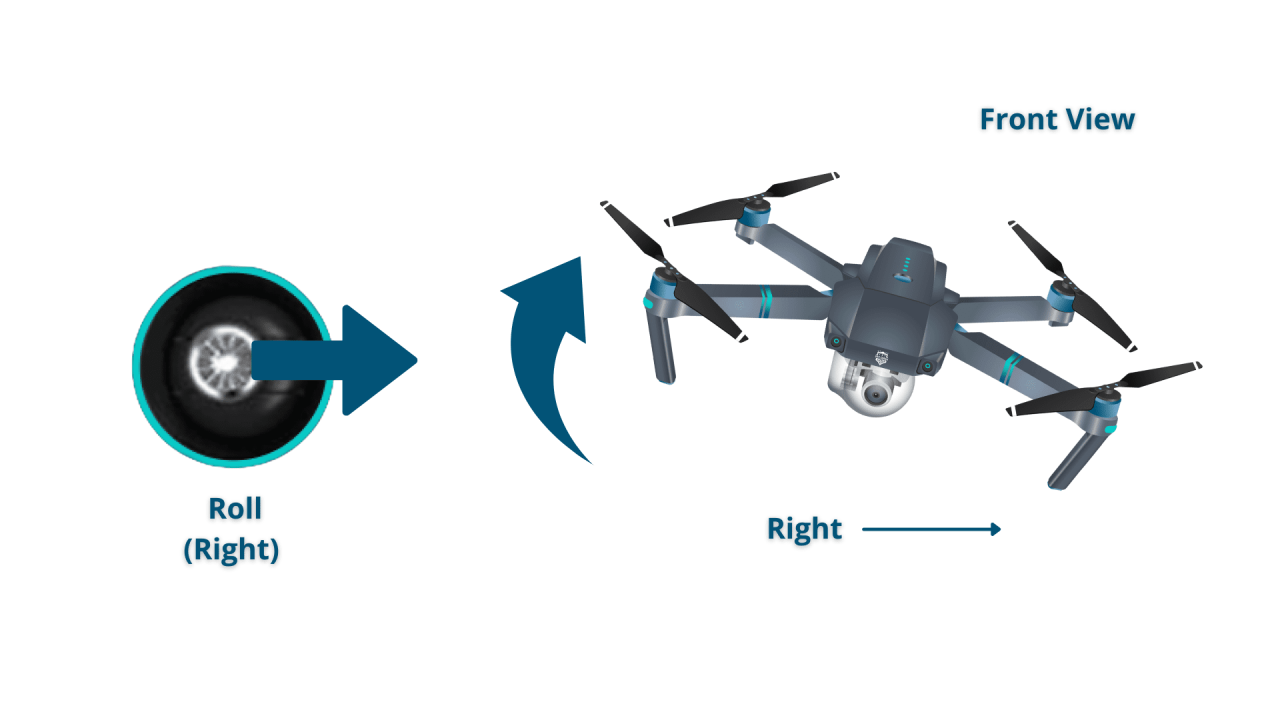
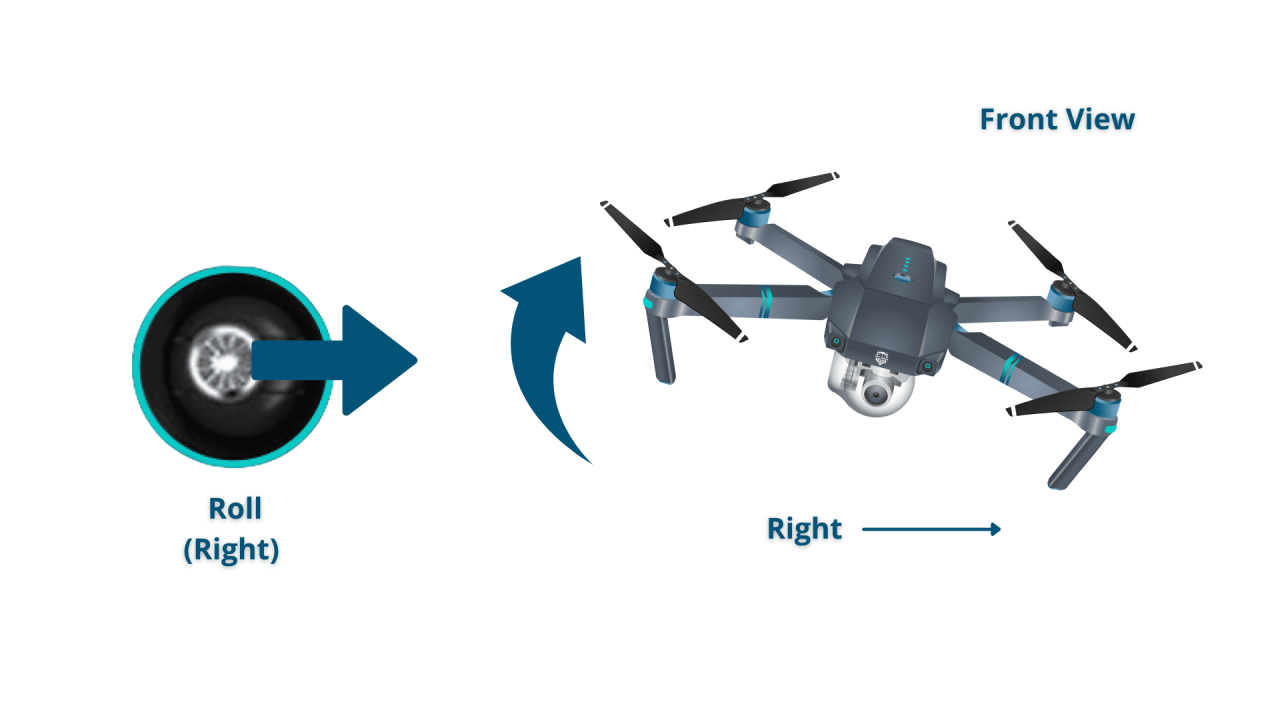
Basic Flight Controls (Throttle, Pitch, Roll, Yaw)
Most drones use four primary controls: throttle (controls altitude), pitch (forward and backward movement), roll (left and right movement), and yaw (rotation around the vertical axis). These controls are typically mapped to sticks on the remote controller. Precise control over these parameters is crucial for smooth and controlled flight.
Taking Off, Hovering, and Landing Safely
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle to lift the drone vertically. Maintain a steady throttle to achieve a stable hover.
- Hovering: Maintain a constant throttle and use subtle adjustments to pitch, roll, and yaw to keep the drone in a fixed position.
- Landing: Gradually reduce throttle to descend slowly and smoothly. Use minimal adjustments to pitch, roll, and yaw to maintain a controlled descent and landing.
Basic Maneuvers (Turning, Ascending, Descending)
- Turning: Use the yaw control to rotate the drone in the desired direction. Combine yaw with roll and pitch for coordinated turns.
- Ascending: Increase throttle to increase altitude.
- Descending: Decrease throttle to decrease altitude.
Comparison of Flight Modes
Different drone models offer various flight modes, each with specific characteristics and functionalities. For example, a “Beginner” mode may limit speed and responsiveness, while a “Sport” mode might allow for faster and more agile maneuvers. Understanding these modes is important for choosing the appropriate setting based on skill level and the intended flight scenario.
Advanced Flight Techniques and Features
Beyond basic flight, drones offer advanced features and techniques that enhance capabilities and flight precision. Mastering these enhances both the operational efficiency and creative potential of the drone.
Advanced Flight Features (Waypoint Navigation, Return-to-Home)
Waypoint navigation allows you to program a flight path by setting a series of waypoints, enabling automated flights along a predefined route. Return-to-Home (RTH) is a safety feature that automatically returns the drone to its home point if the connection is lost or the battery is low.
Flight Modes (Sport, Cine, etc.)
Different flight modes cater to various needs. “Sport” mode typically allows for higher speeds and more aggressive maneuvers, while “Cine” mode prioritizes smooth, cinematic movements. Choosing the right mode depends on the desired flight characteristics and the type of footage being captured.
Techniques for Smooth Video Recording
Smooth and stable video recording requires careful piloting and may involve using features like gimbal stabilization and employing slow, deliberate movements. Avoid sudden changes in speed or direction, and maintain a consistent altitude and speed for optimal results.
Tips for Improving Drone Piloting Skills
- Practice regularly in a safe and open area.
- Start with basic maneuvers and gradually progress to more advanced techniques.
- Utilize simulator software to practice in a risk-free environment.
- Watch tutorial videos and learn from experienced pilots.
- Understand and utilize the drone’s various flight modes.
- Always prioritize safety and responsible operation.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for ensuring the longevity and reliable performance of your drone. This section details routine maintenance and common troubleshooting steps.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Routine maintenance involves regularly inspecting the drone for damage, cleaning the propellers and body, and checking the battery’s health. This includes checking for loose screws, worn-out parts, and any signs of damage from previous flights. Proper storage in a dry and safe environment is also crucial.
Troubleshooting Common Drone Problems
Common issues include low battery, GPS signal loss, and motor malfunctions. Low battery is often solved by charging the battery, GPS signal loss can sometimes be resolved by moving to an area with better signal reception, and motor malfunctions may require professional repair or replacement.
Tips for Safe Drone Storage and Transport
Store the drone in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Use a protective case or bag during transport to prevent damage from bumps and scratches. Always disconnect the battery before storage or transport.
Common Drone Malfunctions, Causes, and Solutions
| Malfunction | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Low Battery | Insufficient charge, high power consumption | Charge battery, reduce flight time |
| GPS Signal Loss | Obstructed signal, poor GPS reception | Move to area with clear sky view, restart drone |
| Motor Malfunction | Motor damage, ESC failure | Inspect motor and ESC, seek professional repair/replacement |
| Unstable Flight | Calibration issues, low battery, wind conditions | Recalibrate compass and sensors, charge battery, fly in calmer conditions |
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. Understanding key factors and techniques is essential for achieving high-quality results.
Factors Affecting Footage Quality
Lighting, composition, and camera settings significantly impact footage quality. Good lighting enhances detail and color accuracy, while careful composition creates visually appealing images. Appropriate camera settings, such as shutter speed, ISO, and aperture, also play a vital role in achieving the desired look and feel.
Tips for Capturing High-Quality Aerial Footage
Plan your shots carefully, considering lighting conditions, composition, and the desired perspective. Use smooth and controlled movements to avoid jerky footage. Experiment with different camera angles and settings to find what works best for your subject and creative vision.
Camera Settings and Their Impact, How to operate a drone
Shutter speed affects motion blur, ISO impacts noise levels, and aperture controls depth of field. Understanding these settings allows you to tailor your footage to specific needs. For example, a faster shutter speed can freeze motion, while a wider aperture can create a shallow depth of field, isolating your subject.
Step-by-Step Guide for Drone Photography/Videography Project
- Plan your shoot: Location scouting, weather check, flight path planning.
- Prepare your equipment: Battery check, camera settings, memory card.
- Conduct a pre-flight check: Safety procedures, GPS signal, compass calibration.
- Execute the flight: Smooth camera movements, consistent altitude and speed.
- Post-processing: Editing, color grading, stabilization.
Successfully operating a drone is a rewarding experience, combining technical skill with creative vision. From the thrill of controlled flight to the artistry of capturing stunning aerial footage, the journey of learning to operate a drone is filled with continuous learning and discovery. Remember to always prioritize safety, adhere to regulations, and continue honing your skills to unlock the full potential of this exciting technology.
The sky’s the limit—literally!
Detailed FAQs
What is the best drone for beginners?
There are many great beginner-friendly drones available. Look for models that are easy to control, have good stability features, and offer a user-friendly interface. Read reviews and compare features before making a purchase.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, weather conditions, and flight style. Typically, you can expect between 15-30 minutes of flight time per battery charge. Always carry extra batteries.
What should I do if I lose GPS signal?
If you lose GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available) and attempt to regain signal. If signal isn’t restored, carefully land the drone in a safe location.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and procedures. Registration is often mandatory for commercial use and may be required for recreational use in some areas.